Name and Describe Each Star Phase
O and B are uncommon very hot and bright. The waning gibbous phase is between a half moon and full moon.

Types Of Stars Stellar Classification Lifecycle And Charts
Name and describe each star phase - 32640691 addie57 addie57 05012021 Science Primary School answered Drag each label to the correct star phase.

. Main sequence stars are in an almost linear line diagonally from upper left to bottom right white dwarfs are just below main sequence in lower left. Be able to explain why it is at each point. The 8 Moon Phases Names.
Punch 6 holes in a piece of cardboard or cotton batting and insert one of the lights through each hole. During the second half of the lunar month the Moon grows thinner each night. Waxing Gibbous still growing.
New the new moon is not visible. In this phase the star can be called an asymptotic giant branch star or sometimes a red supergiant star. The star has now reached the red giant phase.
A smaller star like the Sun will gradually cool down and stop glowing. During these changes it will go through the planetary nebula phase and white dwarf phase. Along with their brightness apparent magnitude the spectral class of a star can tell astronomers a lot about it.
If a star has between 135 and 21 times the mass of the Sun it doesnt form a white dwarf when it dies. The outer shell of the star which is still mostly hydrogen starts to expand. Low and medium-mass stars then evolve into red giants.
The Moon has now completed one half of the lunar month. Besides scientists can spot the star in the T-Tauri phase without the assistance of radio waves and or infrared. The gibbous moon appears to grow fatter each night until we see the full sunlit face of the Moon.
In order of decreasing temperature O B A F G K and M. First Quarter the moon looks like half a circle. The most commonly known phase changes are those six between solids liquids and gasses.
However plasma also is a state of matter so a complete list requires all eight total phase changes. Where would you find a star on an H-R diagram at each stage of its life. Depending on the mass of the star this lifetime ranges from only a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive which is considerably longer than the age of the universe.
Name and describe each star phasered supergiant black hole white dwarfplanetary nebula attracts all matter and energy that come nearby a heavy star that expands and gives off large amounts of light shells that are cast away from a low mass star a low mass star that has shed its outer layers. We call this phase the full moon. Supergiants and giants are in upper right giants slightly below.
When the hydrogen supply in the core begins to run out and the star is no longer generating heat by nuclear fusion the core becomes unstable and contracts. The waxing gibbous phase is between a half moon and full moon. Red super giant star rightarrow supernova rightarrow neutron star or a black hole depending on size A nebula A star forms from massive clouds.
We see the first quarter phase as a half moon. For example the star Antares is an M type supergiant. As it expands it cools and glows red.
Waxing Crescent the Moon starts growing. Instead the star dies in a catastrophic supernova explosion and the. Full we see the entire circle of the Moon lit up.
1 All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Name and describe each star phase What picture do the blue things go. However high-mass stars 10 times bigger than the Sun become red supergiants during their helium-burning phase.
After many thousands of millions of years it will stop glowing and become a black dwarf. Drag each label to the correct image. Waning Gibbous the Moon starts shrinking.
The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. Waning means it is getting. It is red because it is cooler than it was in the main.
It explodes as a supernova. A young star starts to form in the T-Tauri phase and it begins to produce strong winds that push away the surrounding molecule and gas. You might need to tape them in place.
Here are the official 8 Moon Phases in order. There are seven main types of stars. For low mass stars this is the final stage of their lifetime in which they generate energy via fusion.
Matter undergoes phase changes or phase transitions from one state of matter to another. Below is a complete list of the names of these phase changes. It rises almost exactly as the Sun sets and sets just as the Sun rises the next day.
It has a luminosity 13000 times that of the Sun. A massive star experiences a much more energetic and violent end. Waxing means it is getting bigger.
This scatters materials from inside the. To show the birth of a star as a hot gas cloud wrap the outside of a globe in cotton and place it over the first bulb of the string of lights. First Quarter.
Two per each box 2. These high mass stars fuse helium into carbon and oxygen at a faster rate but during periods of slow fusion the star can contract in on itself and become a blue supergiant. Moreover it allows the forming star to become visible for the first time.
We can see the Moon completely illuminated during full moons.

The Our Space On Instagram The Lifecycle Of A Star The Starting Phase For All Stars Including Our S Astronomy Facts Space And Astronomy Black Hole
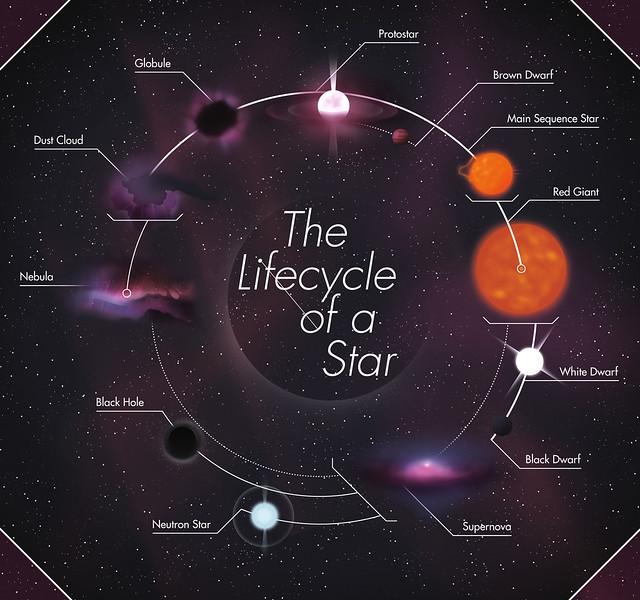
Life Cycle Of A Star Seven Main Stages Of A Star Stellar Evolution Video And Faqs

Types Of Stars Stellar Classification Lifecycle And Charts

Drag Each Label To The Correct Star Phase Name And Describe Each Star Phasewhat Picture Do The Blue Brainly In
No comments for "Name and Describe Each Star Phase"
Post a Comment